Smoking Marijuana May Be Worse for Lungs Than Smoking Cigarettes
Radiological Society of North America
 |
| Airway inflammation and emphysema are more common in marijuana smokers than cigarette smokers, according to new research. |
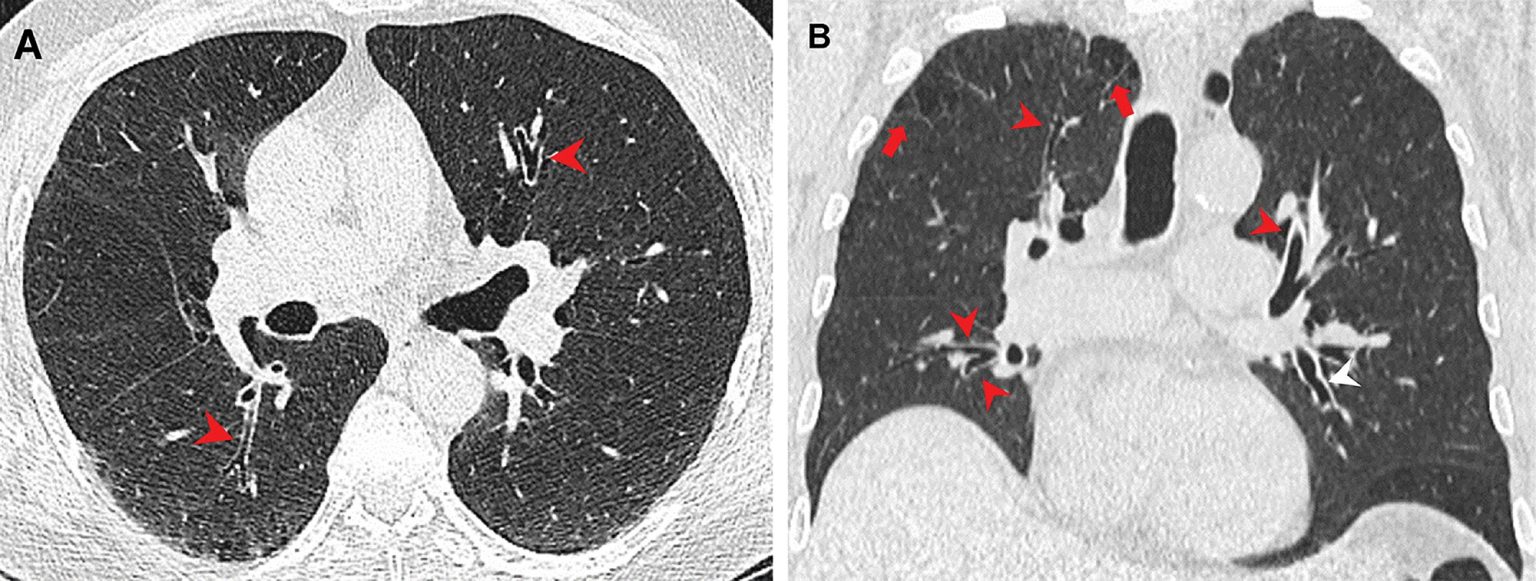
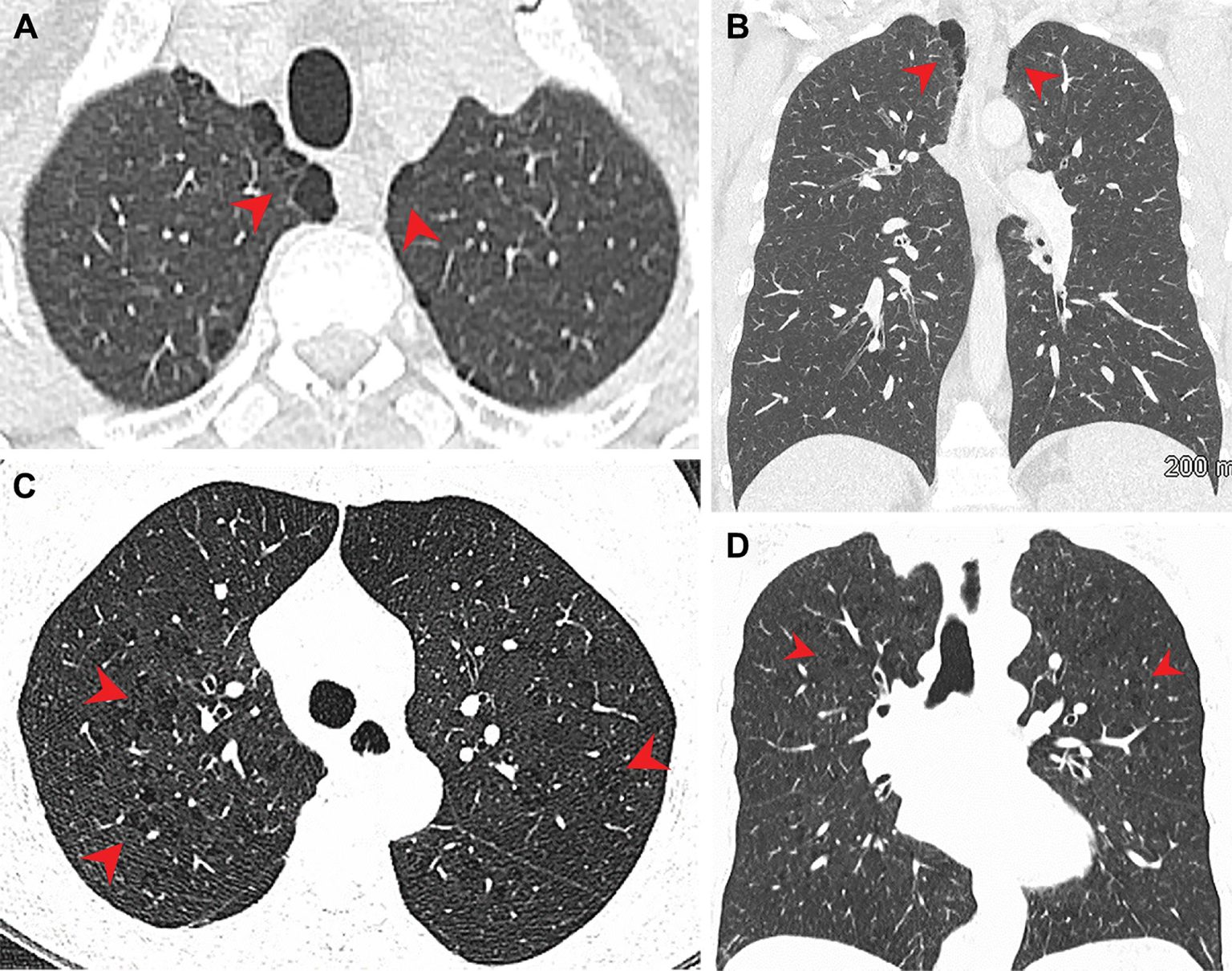
According to new research, airway inflammation and emphysema are more common in marijuana smokers than cigarette smokers. Investigators said the difference may be due to the way that marijuana is smoked and the fact that marijuana smoke enters the lungs unfiltered. The research study was published on November 15 in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Marijuana is the most-commonly smoked substance after tobacco and one of the most widely used psychoactive substances in the world. Amid the legalization of recreational marijuana in Canada and many states in the U.S., its use has increased substantially in recent years. With the growing use, there is an urgent need for information on marijuana’s effects on the lungs, something that is currently lacking.“We know what cigarettes do to the lungs,” said study author Giselle Revah, M.D., a cardiothoracic radiologist and assistant professor at the University of Ottawa in Ottawa, Canada. “There are well-researched and established findings of cigarette smoking on the lungs. Marijuana we know very little about.”To find out more, Dr. Revah and colleagues compared chest CT results from 56 marijuana smokers with those of 57 non-smoking controls and 33 tobacco-only smokers.
Three-quarters of the marijuana smokers had emphysema, a lung disease that causes difficulty with breathing, compared with 67% of the tobacco-only smokers. Only 5% of the non-smokers had emphysema. Paraseptal emphysema, which damages the tiny ducts that connect to the air sacs in the lungs, was the predominant emphysema subtype in marijuana smokers compared to the tobacco-only group.
Airway inflammation was also more common in marijuana smokers than non-smokers and tobacco-only smokers. The same was true for gynecomastia, a condition of enlarged male breast tissue due to a hormone imbalance. Gynecomastia was found in 38% of the marijuana smokers, compared with just 11% of the tobacco-only smokers and 16% of the controls.The researchers found similar results among age-matched subgroups, where the rates of emphysema and airway inflammation were again higher in the marijuana smokers than the tobacco-only smokers.
There was no difference in coronary artery calcification between age-matched marijuana and tobacco-only groups.
According to Dr. Revah, the results were surprising, especially considering that the patients in the tobacco-only group had an extensive smoking history.
The fact that our marijuana smokers—some of whom also smoked tobacco—had additional findings of airway inflammation/chronic bronchitis suggests that marijuana has additional synergistic effects on the lungs above tobacco,” she said.
“In addition, our results were still significant when we compared the non-age-matched groups, including younger patients who smoked marijuana and who presumably had less lifetime exposure to cigarette smoke.”
There are likely several factors that contribute to the differences between the two groups. Marijuana is smoked unfiltered, Dr. Revah noted, while tobacco cigarettes are usually filtered. This results in more particulates reaching the airways from smoking marijuana.
In addition, marijuana is inhaled with a longer breath hold and puff volume than tobacco smoke.
“It has been suggested that smoking a marijuana joint deposits four times more particulates in the lung than an average tobacco cigarette,” Dr. Revah said. “These particulates are likely airway irritants.”
The higher incidence of emphysema may also be due to the way that marijuana is smoked. Full inhalation with a sustained Valsalva maneuver, an attempt at exhalation against a closed airway, may lead to trauma and peripheral airspace changes.
More research is needed, Dr. Revah said, with larger groups of people and more data on how much and how often people are smoking. Future research could also look at the impact of different inhalation techniques, such as through a bong, a joint, or a pipe.
“It would be interesting to see if the inhalation method makes a difference,” Dr. Revah said.
For more on this research, see Emphysema More Common in Marijuana Smokers Than Cigarette Smokers.
Reference: “Chest CT Findings in Marijuana Smokers” by Luke Murtha, Paul Sathiadoss, Jean-Paul Salameh, Matthew D. F. Mcinnes and Giselle Revah, 15 November 2022, Radiology. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.212611